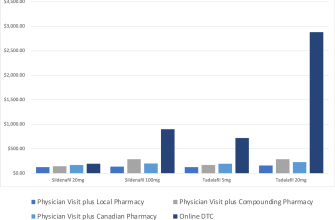
Consider Neurontin (gabapentin) as a potential option for managing symptoms of bipolar disorder. This medication demonstrates promise in alleviating mood swings and stabilizing emotional states. Research indicates its effectiveness, particularly for individuals experiencing anxiety or mood fluctuations. Regular consultation with a healthcare provider ensures that Neurontin aligns with your specific treatment plan.
Integrating Neurontin can enhance overall therapeutic strategies. Patients have reported decreased anxiety and improved sleep patterns while using this medication. This dual benefit can significantly contribute to daily functioning and emotional well-being. It’s crucial to monitor your response to Neurontin and communicate any changes or side effects to your doctor promptly.
Staying informed about the latest findings can guide your treatment approach. Studies suggest that Neurontin may work best alongside traditional mood stabilizers or other medications. This combination could optimize symptom management. Always engage in open discussions with your healthcare provider to tailor your treatment options effectively.
- Neurontin in the Treatment of Bipolar Disorders
- Dosage and Administration
- Potential Benefits and Risks
- Understanding the Role of Neurontin in Mood Stabilization
- Mechanism of Action
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Guidelines and Administration for Bipolar Patients
- Administration Tips
- Long-term Considerations
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions with Other Medications
Neurontin in the Treatment of Bipolar Disorders
Neurontin, known generically as gabapentin, offers potential benefits for individuals with bipolar disorders, particularly in managing mood stability and reducing anxiety. Clinicians often prescribe it as an adjunctive treatment when traditional mood stabilizers alone do not suffice. Gabapentin’s mechanism includes modulating neurotransmitter release, which helps manage mood swings effectively.
Dosage and Administration
A typical starting dose of Neurontin ranges from 300 to 900 mg daily, adjusted based on patient tolerance and response. It’s crucial to titrate doses gradually to minimize side effects, such as dizziness or sedation. Consistent monitoring allows healthcare providers to optimize treatment while ensuring that patients derive maximum benefit from therapy.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Patients may experience decreased frequency and intensity of manic or depressive episodes with Neurontin. Positive effects on sleep quality can also enhance overall mood stability. However, some individuals may face risks, including potential dependency or withdrawal symptoms upon discontinuation. Regular follow-up consultations help in evaluating the ongoing effectiveness of Neurontin and its side effect profile.
Understanding the Role of Neurontin in Mood Stabilization
Neurontin (gabapentin) offers valuable support in managing mood stability for individuals with bipolar disorders. This medication assists in reducing the frequency and severity of mood swings, enhancing emotional regulation.
Mechanism of Action
Neurontin functions by modulating neurotransmitter release, specifically by influencing the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). This action may contribute to a calming effect on the nervous system, which can help mitigate the highs of mania and the lows of depression. Clinical observations indicate that patients often report improved mood stability and decreased anxiety when incorporating Neurontin into their treatment regimen.
Dosage and Administration
Start with a low dosage, gradually increasing based on individual response and tolerability. Regular communication with a healthcare provider is essential for monitoring progress and adjusting the dosage as needed. Many find success with Neurontin as an adjunct to other mood stabilizers or antipsychotic medications, providing a comprehensive approach to mood management.
While Neurontin is well tolerated by many, potential side effects may include dizziness and fatigue. Patients should maintain open discussions with their healthcare team to address any concerns and ensure an optimal treatment strategy.
In summary, Neurontin plays a supportive role in mood stabilization for those with bipolar disorders, enhancing emotional balance and improving quality of life.
Dosage Guidelines and Administration for Bipolar Patients
The initial dose of Neurontin (gabapentin) for bipolar disorder typically begins at 300 mg taken three times a day. This starting dose helps assess tolerance and effectiveness without overwhelming the patient. Adjustments can be made based on clinical response and tolerability.
After a week, the dosage may be gradually increased to 600 mg per day, divided into three doses. Most patients find optimal results between 900 mg and 2400 mg daily, depending on individual needs and sensitivities. It is crucial to avoid abrupt changes in dosage to prevent withdrawal effects or mood destabilization.
Administration Tips
Neurontin can be taken with or without food. Consistency in how the medication is administered aids in maintaining stable blood levels. Encourage patients to set reminders for their doses to promote adherence. If a dose is missed, patients should take it as soon as they remember, unless it is almost time for the next dose; in that case, they should skip the missed one and resume the regular schedule. Doubling up on doses is not recommended.
Long-term Considerations
Continual assessment of mood and any side effects is essential during treatment. Regular follow-ups allow for necessary dose adjustments. Patients should communicate openly with their healthcare provider about any changes they experience, whether positive or negative. This ongoing dialogue ensures that the treatment remains aligned with their needs.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions with Other Medications
Neurontin (gabapentin) can cause various side effects, and it’s crucial to recognize them for proper management. Common side effects include:
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Somnolence
- Peripheral edema
- Weight gain
- Ataxia
Less frequently, patients may experience mood changes, anxiety, or even depression. Any significant mood alterations should prompt immediate consultation with a healthcare provider.
Neurontin may interact with other medications. Key interactions include:
- Opioids: Co-administration can increase the risk of central nervous system (CNS) depression, leading to respiratory issues.
- Antacids: Calcium-based antacids can reduce Neurontin absorption. Take them at least two hours apart.
- Other CNS depressants: Combining with benzodiazepines or alcohol can enhance sedation and dizziness.
Always inform healthcare providers about all medications and supplements being taken to minimize risks. Regular monitoring and consultation can help manage any side effects or interactions effectively.
In case of severe side effects, such as suicidal thoughts or allergic reactions, seek medical attention immediately. Proper management of Neurontin use is crucial for safety and efficacy in treating bipolar disorders.